
Chemical mediators of inflammation - B. Pharma 2nd Semester Pathophysiology notes pdf
Chemical mediators of inflammation
Contents
• Chemical mediators of inflammation
• Cell derived mediators
• Plasma derived mediators
Objectives
At the end of this lecture, student will be able to
• List various chemical mediators of inflammation
• Describe the formation and functions of cell derived mediators
• Describe the formation and functions of plasma derived mediators
Chemical mediators of inflammation
• Endogenous compounds
• Released during inflammation
• Increases vascular permeability
• Edema, Destruction of inflammatory agents
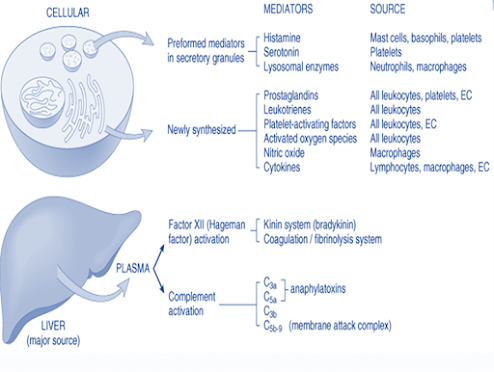
Cell derived mediators
• Vasoactive amines – Histamine, Serotonin, Neuropeptides
• Arachidonic acid metabolites
– Via COX pathway - Prostaglandins, Thromboxane A2, prostacyclin
– Via LOX pathway - 5-HETE, leukotrienes
• Lysosomal system
• Platelet activating factor
• Nitric oxide and oxygen metabolites
Plasma derived mediators of inflammation
• The kinin system
• The clotting system
• The fibrinolytic system
• The complement system
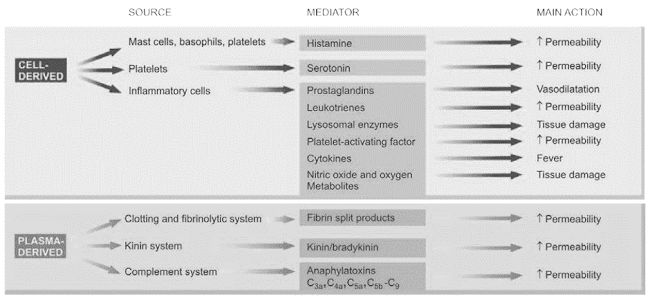
Vasoactive amines (Autocoids)
Amine autocoids
• Histamine
• 5 – HT / Serotonin
Released within 1 hour of inflammatory response
Histamine
• Stored in mast cells, basophills & platelets
Released due to – Heat/cold radiations
– Chemical irritant & immunological reactions
– Anaphyla toxins
Main actions of Histamine
• Vaso dilation
• ↑ permeability of venules
• Itching & pain
• Release of other cell derived mediators
• Broncho constriction
Serotonin
• Present in chromaffin cells of GIT
• In spleen, nervous system, mast cells & platelets
Actions
• Vasodilation
• ↑vascular permeability
• Less potent than histamine
Neuropeptides
• Tachykinin neuropeptides - substance P, neurokinin A, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) & somatostatin
• Produced in the central and peripheral nervous systems
Actions
• Increased vascular permeability
• Transmission of pain stimuli
• Mast cell degranulation
Arachdonic acid Metabolite
• Tissue injury – Phospholipase A2activation
• Conversion of phospholipids into arachdonic acid
Metabolism of arachdonic acid follows 2 pathway
• COX (Cyclo-oxygenase) – Pathway
• LOX (Lipo- oxygenase) – Pathway
COX Pathway
LOX Pathway
Lysosomal components
Granules of Neutrophills
Primary granules
· Myeloperoxidase
· Acid hydrolase
· Neutral proteases
Secondary granules
· Lactoferrin
· Lysozyme
· Alkaline phosphatase
· Collagenase
Granules of Monocytes & Tissue macrophages
• Cells on degranulation releases mediators like
• Acid proteases
• Collagenase
• Elastase
• Plasminogen activator
More involved in chronic inflammation
Platelet Activating Factor (PAF)
IgE-sensitised basophils or mast cells, other leucocytes, endothelium and platelets
• ↑ vascular permeability
• Vasodilatation in low concentration and vasoconstriction
• Broncho constriction
• Adhesion of leucocytes to endothelium
• Chemotaxis
Cytokines
• Group of polypeptide substances
• Produced by activated lymphocytes/ monocytes
• Interleukin 1 & 8
• Tumor necrosis factor
• Interferon
• Platelet factor
Actions:
• IL –I, TNF α& β- ↑ leucocyte adherence, Platelet aggregation, proliferation of fibroblast
• Interferon gamma – activation of macrophages & neutrophils
• IL-8 – Chemotactic of neutrophills
• PF – 4 – Chemotactic for neutrophills, monocytes & eosinophills
Nitric oxide & oxygen metabolites
• Released by activated macrophages from vascular endothelium
• Vasodilation
• Inhibiton of platelet aggregation
• Killing of micro organism
• O2 free radicals released from activated neutrophills & macrophages
• Endothelial damage
• ↑vascular permeability
• Tissue matrix damage
Plasma derived mediators
• Interlinked system
• Include
– Clotting system
– Kinin system
– Fibrinolytic system
– Complement system
• Hageman factor (Factor XII) – connects the other 4 system
Clotting system
• Results in formation of fibrinogen
• Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin & fibrinopeptide
– ↑ vascular permeability
– Chemotaxis of leucocytes
– Anticoagulant activity
Fibrinolytic system
• Activated by plasminogen
• Plasminogen activator – plasminogen – plasmin- breakdown of fibrin - fibrinopeptides or fibrin split products
Actions
– Activation of factor XII
– Splits complement fraction C3to C3a– permeability factor
– Degrade fibrin to form fibrin split products
Complement system
Involves 2 pathways
• Classic pathway through antigen-antibody complexes
• Alternate pathway via non-immunologic agents such as bacterial toxins, cobra venoms and IgA
Anaphylatoxins (C3a, C5a, C4a)
– Activate mast cells and basophils to release of histamine
– cause increased vascular permeability
– augments phagocytosis
• C3b - an opsonin
• C5a - chemotactic for leucocytes
• Membrane attack complex (MAC) (C5b-C9) is a lipid dissolving agent and causes holes in the phospholipid membrane
Chemical mediators of inflammation
Summary
• Chemical mediators are endogenous compounds released during inflammation which increases vascular permeability, bring about edema and destruction of inflammatory agents
• Chemical mediators of inflammation are derived from cell and plasma
• Cell derived mediators include histamine, serotonin, leukotrienes, platelet activating factors, cytokinines, prostaglandins
• Plasma derived mediators include kinin system, cltting and fibrinolytic system and clotting system





0 Comments: