
Quality by Design in Product Development
Quality by Design (QbD) in Product Development
v Systematic, holistic and proactive approach to pharmaceutical development.
v Begins with predefined objectives
v Emphasizes product and process understanding and process control
v Based on sound science and quality risk management
Ref.: ICH Q8 (R2)
Generic industry business model: Regulator’s perspective
v File first, learn later
v Major amendments during review process
- Exhibit batch stability failure, formulation revision
v Longer time for generic product approval
v Approved product may not be marketed
v Post approval changes – prior approval supplements
How QbD will help improve?
v Ensure higher level of assurance of product quality for patient
Ø Improved product and process design & understanding
Ø Monitoring, tracking & trending of product & process.
v More efficient regulatory oversight
v Efficiency and cost saving for industry
Ø Increase efficiency of manufacturing process
Ø Minimize / eliminate potential compliance actions
Overview of QbD
Quality Target Product Profile à Product Design and Understanding à Process Design and Understanding à Control Strategy à Continuous Improvement
v Quality Target Product Profile (QTPP)
v Define Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs)
v Perform risk assessment
v Link raw material attributes and process parameters to CQAs
v Design and implement a control strategy
v Manage product lifecycle, including continuous improvement
Quality Target Product Profile-QTPP
What is QTPP?
• A set of elements that defines the drug product
• The target or goal set in advance
• A guide to Drug Product development
What forms the basis for QTPP?
• The RLD and its label
• Applicable regulatory guidelines
When to define QTPP?
• At the start of development
• Knowledge gained in development may change some elements
Components of QTPP
Components related to safety, efficacy, identity, purity and potency
Critical and non-critical components, e.g.
• Critical: Assay, content uniformity
• Non-critical: Appearance
Fixed and variable components
• Fixed elements must be present
e.g. Dosage form, strength
• Variable elements may have a range of acceptable values
e.g. Tablet weight, assay
QTPP components for IR tablet – Example
| Dosage Form |
| Route of administration |
| Strength |
| Weight |
| Pharmacokinetics |
| Appearance |
| Identity |
| Assay |
| Impurities |
| Content uniformity |
| Friability |
| Dissolution |
| Residual solvents |
Specific requirements in QTPP
v Scored tablets
Ø Weight variation between two halves
Ø Dissolution of half tablet
v Orally Disintegrating tablets
Ø Hardness
Ø Disintegration time
Ø Container closure
v Extended Release products
Ø Alcohol induced dose dumping
Critical Quality Attributes – CQAs
v CQAs are a subset of the QTPP
v Include critical parameters that are likely to change based upon variations in raw materials and processes
-Identity test for dosage form – Not a CQA
-Assay, Content uniformity – CQAs
v CQAs are monitored throughout the DP development.
v CQAs ensure that DP remains within safe and effective levels.
QTPP and CQAs
| QTPP components |
| Dosage Form |
| Route of administration |
| Strength |
| Weight |
| Pharmacokinetics |
| Appearance |
| Identity |
| Assay |
| Impurities |
| Content uniformity |
| Friability |
| Dissolution |
| Residual solvents |
â
| CQAs |
| Assay (efficacy) |
| Impurities (safety) |
| C.U. (efficacy) |
| Dissolution (efficacy) |
QTPP and Specifications
QTPP
• Desired target for developmental work
• Components of QTPP may or may not be in specification
- Not in spec – Dosage form, strength
- In spec – Assay, impurities
• Does not include acceptance criteria
Specifications
• Includes all of the CQAs
• Specification is a list of
- tests,
- references to analytical procedures
- acceptance criteria
• Establishes the set of criteria to which DP should conform to be considered acceptable for its intended use
• Defining a QTPP does not mean setting all acceptance criteria
• or the product specifications before development work begins.
QbD Tools – Risk Assessment
Why risk assessment in product development?
v To identify relative risk levels at the beginning of product development
v To prioritize limited development resources
v To document the decision making process throughout development
v To assess the needs of additional studies for scale up and technology transfer
v To identify appropriate specifications, critical process parameters and manufacturing controls
v To decrease variability of critical quality attributes
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment for
• Formulation – starting material properties, levels of components
• Manufacturing process
Steps for risk assessment
• List out all components / processes
• Prepare the process flow chart
• Identify all potential failure modes for each item with risk query (what might go wrong?)
• Risk analysis
• Risk evaluation
Various formal methodologies available for risk assessment
v Failure Mode Effects Analysis & Failure Mode Effects & Criticality Analysis
v Hazard & Operability Analysis
v Supporting statistical tools
• It is neither always appropriate nor always necessary to use a formal risk management process….. The use of informal risk assessment processes can also be considered acceptable. – ICH Q9
• A risk-based justification based on experience and data is always necessary!
Quality by Design for ANDAs:
An Example for Immediate-Release Dosage Forms
v Generic product development for Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg.
v Acetriptan is a BCS Class II compound displaying poor aqueous solubility (less than 0.015 mg/mL) across the physiological pH range.
v It exists in three different polymorphic forms which may affect dissolution.
v Polymorph III is the most stable polymorph.
v Drug product is prepared with roller compaction process.
Risk assessment for formulation components
| Drug Product CQA | Formulation Variables | ||||
| Drug Substance PSD | MCC/Lactose Ratio | CCS Level | Talc Level | Magnesium Stearate Level | |
| Assay | MEDIUM | MEDIUM | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| Content Uniformity | HIGH | HIGH | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| Dissolution | HIGH | MEDIUM | HIGH | LOW | HIGH |
| Degradation Products | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | MEDIUM |
Risk assessment of DP manufacturing process
| Drug Product CQAs | Process Steps | ||||
| Pre-RC* Blending and Lubrication | Roller Compaction | Milling | Final Blending and Lubrication | Compression | |
| Assay | MEDIUM | LOW | MEDIUM | LOW | MEDIUM |
| Content Uniformity | HIGH | HIGH | HIGH | LOW | HIGH |
| Dissolution | MEDIUM | HIGH | MEDIUM | HIGH | HIGH |
| Degradation Products | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
Justification for assigned risks
| Process Steps | Drug Product CQAs | Assigned Risk | Justification |
| Pre-Roller Compaction Blending and Lubrication | Assay | MEDIUM | Suboptimal pre-roller compaction blending and lubrication may cause variable flowability of the blend affecting Assay. |
| Content Uniformity | HIGH | The PSD and cohesiveness of the drug substance adversely impact its flowability. If not blended properly with excipients, it may affect CU. | |
| Dissolution | MEDIUM | Blending process variables may impact the distribution of CCS in the blend which could impact disintegration of the granules and ultimately, dissolution of the tablets. | |
| Degradation Products | LOW | Blending process variables are unrelated to the degradation products of Generic Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg. |
CMAs, CPPs and CQAs
What factors affect drug product CQAs?
v Properties of Input Materials- Identify Critical Material Attributes (CMAs)
v Properties of in-process materials- CQAs of one step become CMAs for a downstream unit operation
v Manufacturing process parameters- Identify Critical Process Parameters (CPPs)
Critical Material Attributes (CMAs)
Risk Assessment of the drug substance attributes
| Drug Product CQAs | Drug Substance Attributes | |||||
| Solid State Form | Hygroscopicity | Particle Size | Residual Solvents | Process Impurities | Chemical Stability | |
| Physical Attributes (size and splitability) | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| Assay | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| Content Uniformity | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
| Drug Release | HIGH | LOW | HIGH | LOW | LOW | LOW |
Solid state form and particle size of DS are CMAs
CPPs
• Risk assessment of manufacturing process
• Identify high risk steps (unit operation) that affect the CQAs of DP.
| Drug Product CQAs | Process Steps | ||||
| Pre-RC* Blending and Lubrication | Roller Compaction | Milling | Final Blending and Lubrication | Compression | |
| Assay | MEDIUM | LOW | MEDIUM | LOW | MEDIUM |
| Content Uniformity | HIGH | HIGH | HIGH | LOW | HIGH |
| Dissolution | MEDIUM | HIGH | MEDIUM | HIGH | HIGH |
| Degradation Products | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
Process Step: Compression
| CPPs | DP CQAs | Risk Assessment | Justification and Strategy |
| Main compression force | Content Uniformity | LOW | CU is dominated by BU and flowability and is unrelated to main compression force. |
| Dissolution | HIGH | Suboptimal compression force may affect tablet hardness and friability and, ultimately, dissolution. | |
| Press speed (dwell time) | Content Uniformity | HIGH | A faster than optimal press speed may cause inconsistent die filling and weight variability which may then impact CU and dissolution. For efficiency, the press speed will be set as fast as practically possible without adversely impacting tablet quality. |
| Dissolution | HIGH |
Control Strategy
“A planned set of controls, derived from current product and process understanding that ensures process performance and product quality…..”
ICH Q8 (R2) & Q10
Control Strategy includes following elements (but not limited to):
• Input material attributes (e.g. drug substance, excipients, container closure)
• Equipment operating conditions (process parameters)
• In-process controls
• Finished product specifications
• Controls for each unit operations
• Methods and frequency of monitoring and control.
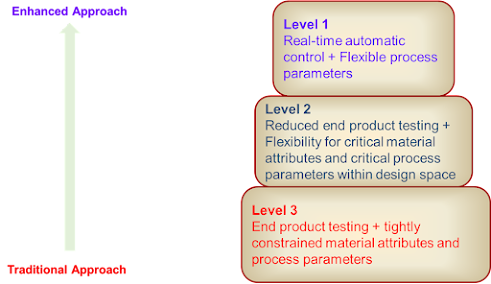
Control Strategy Implementation Options
QbD Tools – DoE
Design of experiments (DoE)
• Useful for screening of variables with significant impact on DP CQAs
• Classical approach uses OFAT (One Factor At A Time)
• Limited number of experiments gives limited information.
• DoE helps study effects of interaction of multiple factors at a time
• Used in optimization studies, enables creation of “design space”
• “Design space” is proposed by the applicant and subject to regulatory assessment and approval.
• “Design space” developed at lab or pilot scale can be proposed for commercial scale, but needs to be verified at production scale for scale dependant parameters.
Process Analytical Technology (PAT)
Ø Timely measurements during processing
v Critical quality and performance attributes
v Raw and in-process materials
Ø At-line, on-line or in-line measurements
• Founded on “Process Understanding”
Opportunities for improvement
• More reliable and consistent processes (& product)
• Less failures, less reworks, less recalls
• Flexibility w.r.t. scale and equipment
• Better / faster Quality Systems
• Process Enhancement Opportunities
PAT in Tablet manufacturing
| Stage | Technique | Measurement |
| Dispensing | NIR / Raman | Identification of raw materials |
| Wet Granulation | NIR | Moisture distribution |
| Drying | NIR | Moisture content |
| Blending | NIR | Blend Uniformity |
| Compression | Strain gauges | Compression force |
| NIR | Content Uniformity |
PAT Examples
Spectral Probe NIR Analyzer installed on viewing window of Glatt FBD without any dryer modification.
Real-time Blend Uniformity by using TruProcess™ Analyzer
QbD: Required or Optional?
Required
• Quality target product profile (QTPP) including critical quality attributes (CQAs) of the drug product and including Product design and understanding
• Product design and understanding
• Critical material attributes (CMAs) of the drug substance and excipients
• Process design and understanding
• Critical process parameters (CPPs)
• Control strategy, including justification
Optional
• Design Space
• Process Analytical Technology
References for QbD
- Guidance for Industry: Q8(R2) Pharmaceutical Development
- Guidance for Industry: Q9 Quality Risk Management
- Guidance for Industry: Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System
- Guidance for Industry PAT: A Framework for Innovative Pharmaceutical Development, Manufacturing, and Quality Assurance
- Quality by Design for ANDAs: An Example for Modified Release Dosage Forms
- Quality by Design for ANDAs: An Example for Immediate Release Dosage Forms
- GPhA presentations
- Draft QbR updated





0 Comments: