
Hepatitis - B. Pharma 2nd Semester Pathophysiology notes pdf
Hepatitis
Contents
• Hepatitis
• Symptoms
• Structure of HBV
• Stages
• Types
Objectives
At the end of this lecture, students will be able to –
• Identify the symptoms of hepatitis
• Describe the structure of HBV
• Explain different stages of hepatitis
Hepatitis
• Inflammation of liver
• Results in damage to hepatocytes with subsequent cell death
Etiology of hepatitis
• Viral infections – Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E ; Epstein barr virus, yellow fever virus, cytomegalo virus & herpes virus
• Autoimmune chronic hepatitis
• Toxins , Alcohol
• Drugs used for the treatment of tuberculosis e.g. Isoniazid
Symptoms of hepatitis
| Initial symptoms | Final symptoms |
| Hepatic symptoms are flu like | Jaundice |
| Mild fever, Chills | Dark urine |
| Headache | Pale faeces containing puss cells |
| Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhoea | Pruritis |
| Anorexia, Fatigue | Enlargement of spleen |
| Slight abdominal pain | Urticaria |
| Aching of joints | Dizziness, Drausiness, circulation problem |
Types of hepatic viruses
| Name of virus | Content | Mode of spread |
| Hepatitis A virus (HAV) | RNA | Faeces |
| Hepatitis B virus (HBV) | DNA | Parenteral, Sexual contact, Blood transfusion, Babies born to HBV infected mothers |
| Hepatitis C virus (HCV) | RNA | Parenteral transmission, IV drug abuse, needle sharing |
| Hepatitis D virus (HDV) | RNA | Super infection |
| Hepatitis E virus (HEV) | RNA | Transmitted enterically |
| Hepatits G virus (HGV) | RNA | Parenterally transmitted hepatotropic virus |
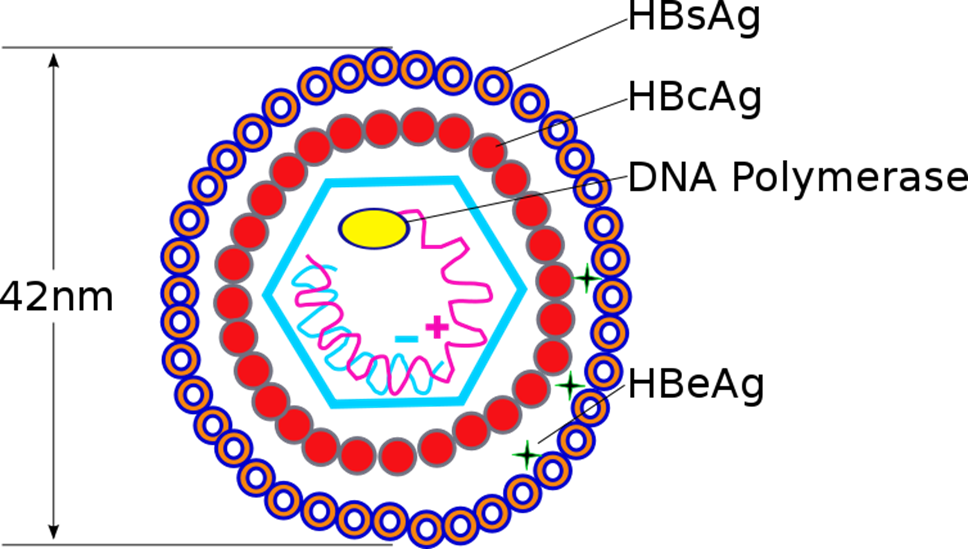
Structure of HBV
• Only DNA containing virus
• Belongs to group ‘hepadnaviridae’
• Diameter- 42 nm; incubation period is 6-8 weeks
• Comprises of core and a capsule
• Core consists of DNA & DNA polymerase
• Core is surrounded by markers
– Hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg)
– Hepatitis B envelope antigen (HBeAg)
– Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBs Ag)
Mode of transmission of
• Present in all body secretion
• A close contact with an infected person spreads the disease
• By blood transfusion
• Not through fecal matter
Stages of hepatitis (Assessed by different markers)
Stage 1
• HBs Ag is identified in asymptomatic phase
• It appears even before the onset of a disease
• Reaches the peak level during disease stage
• The counts become less with in 3-6 months
Stage 2
• HBe Ag, HBV DNA, DNA polymerase appears
• HBe Ag – indicates the progression of infection
• Continues viral replication
Stage 3
• IgM and anti HBc is detected
• Ab is identified just before the onset of symptoms
• After several months of infections IgG and anti HBc
Phases of HBV infection
Proliferative phase
• Shows the presence of symptoms
• DNA of HBV has accessory replicative chromosomes and forms virions
• HBsantigen binds with MHC class molecule and activated CD8+ T-cells
Integrative phase
• Viral DNA gets incorporated into the host genome
• Damage of hepatocytes by activation of CD8+ T- cells
Types of Hepatitis
Acute hepatitis – comprises of 4 phases
1. Incubation period–depends on type of virus
• HAV – 12 weeks
• HBV – 10 weeks
• HCV – 7 weeks
• HDV – 6 weeks
• HEV – 2-8 weeks
Patient does not show any signs or symptoms in incubation period
2. Symptomatic pre – icteric phase
• Non specific symptoms like fatigue, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, low fever, headache, muscle & joint aches, diarrhoea
3. Symptomatic icteric phase
• Yellow coloration appears
• Jaundice appears in 3rd stage
4. Phase of recovery
• Takes place depending upon the severity of infection
Chronic hepatitis
• Hepatic diseases remain for more than 6 months
• Inflammation & necrosis takes place
• Fatigue, Malaise, Lack of apetite, mild jaundice
• Symptoms are highly variable & not predictive in nature
Summary
• Hepatitis is inflammation of liver that results in damage to hepatocytes with subsequent cell death
• It may occur due to viral , autoimmune chronic hepatitis, Toxins, Alcohol and drugs
• HBV is main causative organism
• Types of hepatitis include acute and chronic


0 Comments: