Syphilis
• Syphilis usually is acquired by sexual contact with infected mucous membranes or cutaneous lesions
• It can be acquired by nonsexual personal contact, accidental inoculation, or blood transfusion.
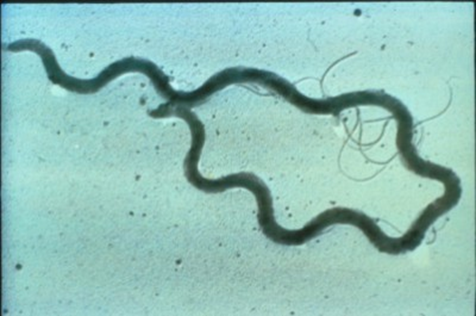
• Treponema pallidum spirochete
• penetrates the intact mucous membrane or a break in the cornified epithelium
• Spirochetemia occurs
Treponema pallidum spirochete
Primary Syphilis
• Primary lesion develops at the site of inoculation
– Progresses from macule to papule to ulcer
– Typically painless, indurated, and has a clean base
– Highly infectious
– Heals spontaneously within 1 to 6 weeks
– 25% present with multiple lesions
• Regional lymph adenopathy: classically rubbery, painless, bilateral
• Serologic tests for syphilis may not be positive during early primary syphilis
Secondary Syphilis
• Secondary lesions occur 3 to 6 weeks after the primary chancre appears
• May persist for weeks to months
• Primary and secondary stages may overlap
• Mucocutaneous lesions most common
• Manifestations
• Rash (75%-100%)
• Lymphadenopathy (50%-86%)
• Malaise
• Mucous patches (6%-30%)
• Alopecia (5%)
Latent Syphilis
• Host suppresses the infection enough so that no lesions are clinically apparent
• Only evidence is positive serologic test for syphilis
• May occur between primary and secondary stages, between secondary relapses, and after secondary stage
• Categories:
– Early latent: <1 year duration
– Late latent: ³1 year duration
Congenital Syphilis
• T. pallidum is transmitted from a pregnant woman with syphilis to fetus
• Stillbirth, neonatal death, and infant disorders
• deafness, neurologic impairment, and bone deformities
• Fetal infection can occur during any trimester of pregnancy
– Early lesions (most common): Infants <2 years old; usually inflammatory
– Late lesions: Children >2 years old; tend to be immunologic and destructive
Summary
• Syphilis usually is acquired by sexual contact with infected mucous membranes or cutaneous lesions
• Causative organism include Treponema pallidum spirochete
• Syphilis is classified as primary, secondary, latent and congenital


0 Comments: