
Asthma - B. Pharma 2nd Semester Pathophysiology notes pdf
Asthma
Contents
• Asthma
• Pathophysiology
• Symptoms
Objectives
At the end of this PDF Notes, student will be able to
• Define Bronchial asthma
• Explain the pathophysiology of Bronchial asthma
• Describe the symptoms of Bronchial asthma
Asthma
• Disorder of the respiratory system that leads to episodic difficulty in breathing
• Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which many cells and cellular elements play a role
• Mast Cells, Eosinophils, T Lymphocytes, Macrophages, Neutrophils , Epithelial Cells
Bronchial Asthma
ü Also called reversible airway obstruction
ü Clinical syndrome characterized by recurrent bouts of bronchospasm
ü Increased responsiveness of the tracheobronchial smooth muscles to various stimuli
ü Results in narrowing of the airway
ü Chronic inflammatory disorder with reversible airflow obstruction
ü Inflammation of bronchial wall mediated by eosinophils, mast cells & lymphocytes
ü Hyper-responsiveness of bronchi – narrow readily with stimuli
ü In late stages – irreversible
Etiology
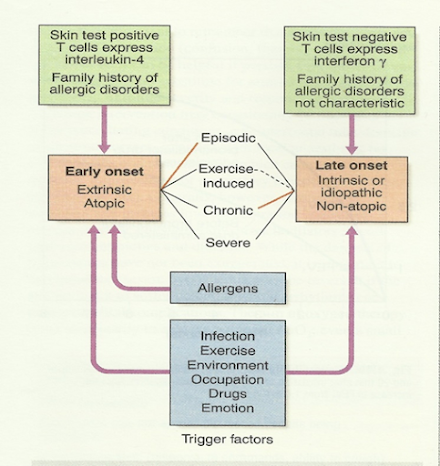
ü History of `atopy` in childhood
ü Family history of allergies
ü Positive skin test
ü Raised IgE level
ü Below 30 years of age
ü Less prone to status asthmaticus
Intrinsic or idiosyncratic
ü No family history of allergy
ü Negative skin test
ü No rise in IgE level
ü Middle age onset
ü Prone to status asthmaticus
Triggers
Drugs
Aspirin, ibuprofen and other prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors, beta blockers
Foods
Nuts, fish, sea food, dairy products, food colouring
Other industrial chemicals
Wood or grain dust, cotton dust, cigarette etc
Miscellaneous
Cold, exercise, hyperventilation ,viral respiratory tract infections, emotion or stress
Pathophysiology
Main features of asthma:
– Hypertrophy of bronchial smooth muscle
– Hyperplasia of epithelial cells
– Mucus gland hypertrophy
– Airway oedema
– Acute bronchoconstriction
– Impaired mucociliary clearance
• Early exposure to
- Allergens
- Viral infections
- Diet induced
• Early onset: Atopic
-Positive family history
-Readily form IgE to common allergens react with mast cells on surface & activate IgE – histamine release
-Many more mediators
v Changes in the airway
ü Epithelial shedding
ü Airway hyper-responsiveness
ü Microvascular leakage – exudate mucus plugging
ü Neuronal imbalance – bronchoconstriction
v IgE-antibody-mediated reaction on the surface of the mast cell leads to release of mast cell components
v Histamine - triggers rapid bronchoconstriction
v Eosinophils release LTC4 and PAF
v Epithelial damage and thick viscous mucus produced causing deterioration in lung function
v Epithelial damage
v Increases access of various irritants to the cholinergic receptors,
v Bronchoconstriction mediated by the parasympathetic nervous system
Signs and Symptoms
• Persistent cough
• Dyspnoea - difficulty in breathing
• Wheezing - a high pitched noise due to turbulent airflow through a narrowed airway
• Tightness of chest
• Shortness of breath
• During attacks - fatigue, cyanosed, lethargic, confused, breathless, rapid breathing (> 30 breaths/minute)
Clinical Features of
• Episodic or chronic
• Triad of:
- Dyspnea (difficulty in breathing)
- Wheezing (additional sounds)
- Cough (persistent)
• Productive sputum
• Others
Tachycardia
Pulsus paradoxus
Sweating
Cyanosis, bradycardia in severe cases
Silent chest
SUMMARY
• Chronic inflammatory disorder with reversible airflow obstruction
• Inflammation of bronchial wall mediated by eosinophils, mast cells & lymphocytes
• IgE-antibody-mediated reaction
• Release of mast cell components which triggers rapid bronchoconstriction
• Persistent cough, recurrent episodes of difficulty in breathing associates with wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, abnormal lung function are the common symptoms







0 Comments: