
Diazotization Titrations - Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 B. Pharma 1st semester
Diazotization Titrations
Contents
• Diazotization titration
• Principle involved
• Preparation & Standardization of Sodium nitrite solution
• Types of diazotization titrations
• Applications
Objectives
By the end of this lecture, students will be able to:
• Explain the principle involved in Diazotisation titrations
• Outline the method of preparation and standardization of sodium nitrite standard solution
• Brief the applications of diazotization titrations
Diazotization Titrations
• Carried out for the estimation of drugs containing primary aromatic amino group
• Several drugs contain primary amino group or
• Can be converted to have such groups by simple reactions
• Like hydrolysis, reduction, etc
• Resulting amino group is diazotized by reaction with sodium nitrite solution in cold acid solution
• Nitrous acid formed diazotizes the compound
• End point can be determined by using external indicator method using starch iodide paper
• Alternatively, potentiometric method or dead stop end point technique can be used
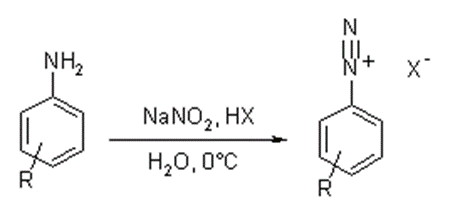
Principle
• General reaction of diazotization,
• Addition of sodium nitrite to hydrochloric acid causes formation of nitrous acid
• Nitrous acid formed diazotizes the aromatic amino group
• After end point, excess nitrous formed is shown by instant formation of blue color with starch iodide paper
• Starch iodide paper is prepared by immersing a filter paper in starch mucilage and potassium iodide solution
• Color change of indicator paper is because of the reaction
• KI + HCl àKCl + HI
• 2HI + 2HNO2 àI2 + 2NO + 2H2O
• Iodine formed reacts with starch mucilage to give the blue color
• End point can also be determined by dead stop end point technique
• Here a potential of 30-50 mV is applied across two platinum electrodes
• Automatic pipette is used for the delivery of nitrite solution
• At the end point delivery of nitrite solution stops automatically
Preparation & Standardization
Preparation of 0.1M sodium nitrite solution
• 7.5 g of sodium nitrite is dissolved in sufficient water to produce 1000 ml
Standardization of 0.1M sodium nitrite solution
• About 0.5 g of sulphanilamide (previously dried at 105 0C for three hours) is transferred to a suitable beaker
• 50 ml of water and 20 ml of HCl is added, stirred until it dissolves
• Cooled to 15 0C
• Contents of beaker are titrated against 0.1M sodium nitrite solution
• Each ml of 0.1M sodium nitrite solution = 0.01722 g of sulphanilamide
Diazotisation Titration
• Specified amount of drug is dissolved in about 50 ml of water and 20 ml of HCl
• Solution is stirred and cooled to about 15 0C
• Mixture is titrated against 0.1M sodium nitrite solution
• End point is determined by
• Using external indicator- starch iodide paper
• Electrometric technique by using platinum electrodes
Types of Diazotization Titrations
Direct titrations
• Here, direct titration of amine in acid against sodium nitrite solution
Reverse method
• Here, solution of amine and sodium nitrite are run into a solution of acid
• Method is used when diazonium salts are insoluble
• For example, naphthylamine sulphonic acids
Special method
• Aminophenols are readily oxidized by nitrous acid to quinones
• For such substances, titration is carried out in the presence of copper sulfate
• It forms diazo oxide
• Diazo oxides are more stable and undergo diazo coupling reaction
Applications of diazotization titrations
1. Direct titration with sodium nitrite solution
• Benzocaine
• Dapsone
• Primaquine phosphate
• Procaine
• All sulpha drugs containing free aromatic amino group like sulfacetamide, sulfadiazine, sulfamethoxazole, etc
2. Conversion of amino group by chemical reactions
A. By reduction
• Metronidazole
• Secnidazole
• Chloramphenicol
• These drugs contain nitro group
• Can be reduced by using any reducing agent to get primary amino group
• Primary aromatic amino group can be diazotized by sodium nitrite
B. Hydrolysis
• Paracetamol (acetyl derivative)
• Phthalyl sulphathiazole (phthalyl derivative)
• Succinyl sulphathiazole (succinyl derivative)
• These drugs are derivatives of amino groups
• Like acetyl or phthalyl or succinyl derivative
• After hydrolysis to free amino group can be titrated with sodium nitrite
• Isocarboxazid- acid solution of the drug liberates benzylhydrazine which can be diazotized to give benzylazide
SUMMARY
• Carried out for the estimation of drugs containing primary aromatic amino group
• Resulting amino group is diazotized by reaction with sodium nitrite solution in cold acid solution
• End point can be determined by using external indicator method using starch iodide paper
• Addition of sodium nitrite to hydrochloric acid causes formation of nitrous acid
• Nitrous acid formed diazotizes the aromatic amino group
• Starch iodide paper is prepared by immersing a filter paper in starch mucilage and potassium iodide solution

0 Comments: