
INTRODUCTION TO QUALITY AND ITS IMPORTANCE
INTRODUCTION TO QUALITY AND ITS IMPORTANCE
• There are so many definitions for Quality.
• Quality is…..
– Based on judgments by an individual or organisation
– Fitness for purpose
– Corresponds to a rating
– Based on acceptable performance
– Meeting goals
– Meeting requirements
What is Quality Assurance?
• What is Quality?
Quality is the ability of your product to be able to satisfy your users
• What is Quality Assurance?
Quality Assurance is the process that demonstrates your product is able to satisfy your users
What is the Aim of QA?
• When good Quality Assurance is implemented there should be improvement in usability and performance and lessening rates of defects
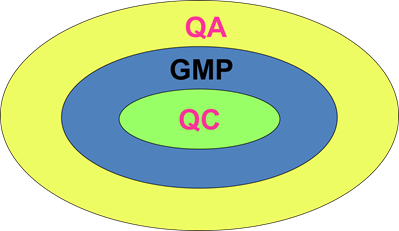
QUALITY TERMINOLOGY
• Quality Control = Correction
• Quality Assurance = Prevention
• Quality Management = Enhance Customer Satisfaction and Continual Improvement
WHAT DOES QA GIVE?
– Quality’ means measure of excellence or state of being free from defects or significant variations.
– But ‘quality assurance’ needs documented standards and best practices to be meaningful
– ‘Quality’ & ‘Best Practice’ can be considered in terms of being ‘Fit for Purpose’
WHAT IS QUALITY CONTROL?
• Quality Control (QC) is the implementation of regular testing procedures against your definitions of quality and more specifically the refinement of these procedures
– Formal use of testing
– Acting on the results of your tests
– Requires planning, structured tests, good documentation
– Relates to output - Quality Circle
– Standards - ISO 9000 & BS5750
• however there is currently no such standard for Web sites
QUALITY RELATIONSHIPS
Quality Management
â
Quality Assurance
â
GMP
â
Quality Control
FACTORS IN DRUG QUALITY ASSURANCE
DRUG PRODUCT QUALITY
– IMPORT & EXPORT CONTROL
– PACKAGING
– LABELLING & PRODUCT INFORMATION
– QC & ANALYSIS
– TRANSPORT DISTRIBUTION DISPENSING & USE
– STORAGE
– MANUFACURING PROCESSES & PROCEDURES
– RAW MATERIALS
– HUMAN RESOURCES- PROFESSIONALS
– LEGISLATIVE FRAMEWORK –REGULATIONS
Quality Assurance: Essential at All Stages
PRINCIPLES OF QUALITY ASSURANCE
• Customer focus
• Leadership
• Involvement of people
• Process approach
• System approach to management
• Continual improvement
• Factual approach to decision making
• Mutually beneficial supplier relationship
COMPONENTS OF QUALITY ASSURANCE
• STRUCTURE EVALUATION
• PROCESS EVALUATION
• OUTCOME EVALUATION
MODELS OF QUALITYASSURANCE
1. System Model
2. Input
3. Throughput
4. Output
5. Feedback
QUALITY ASSURANCE MODEL
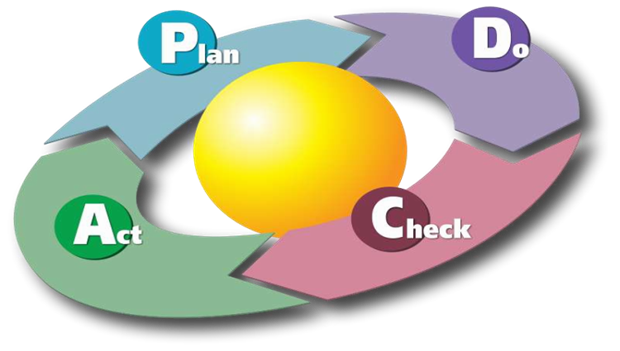
PLAN, DO, STUDY, ACT CYCLE
LEVELS OF EVALUATION OF QUALITY OF CARE
National Level
Trust or organization level
Local Level
APPROACHES OF QUALITY IMPROVEMENT
General Approaches
• Credentialing
• Licensure
• Accreditation
• Certification
• Charter
• Academic Degrees
Specific Approaches
• Peer Review Committees (Staff Review Committees)
• Standard as a device for quality assurance



0 Comments: