
Cell Injury Homeostasis - B. pharma 2nd year Pathophysiology notes pdf
Cell Injury Homeostasis
Content
• Components involved in homeostasis
• Mechanism involved in the Homeostasis
• Positive feedback mechanism
• Negative feedback mechanism
Objectives
At the end of this lecture student will be able to –
• Describe the components of homeostasis system
• Explain mechanism involved in the internal environment maintenance
• Describe feedback loop
HOMEOSTATIC CONTROL MECHANISMS
HOW HOMEOSTATIC CONTROL MECHANISMS WORK?
• Homeostatic control mechanisms work through ‘Feedback Mechanisms’.
• Status of a body condition is continually monitored, evaluated, changed, re-monitored & reevaluated.
FEEDBACK MECHANISM
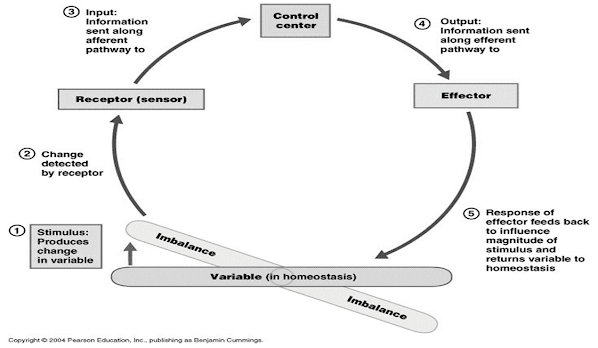
• A feedback mechanism is a cycle in which the output of a system “feeds back” to either modify or reinforce the action taken by the system.
• A feedback mechanism may operate at:
– Tissue level
– Organ level
– Organ system level
– Body level, integrating with other organ systems.
– Feedback mechanism can be:
– Negative feedback (more common)
– Positive feedback
A FEEDBACK SYSTEM CONSISTS OF THREE COMPONENTS
- SENSOR (RECEPTOR): detects specific changes (stimuli) in the environment.
- INTEGRATOR: act to direct impulses to the place where a response can be made.
- EFFECTOR: performs the appropriate response.
A FEEDBACK LOOP
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
• Mechanisms that maintain the factor at some mean value.
• Reverse a change
• Restore abnormal values to normal
EXAMPLE: NEGATIVE FEEDBACK BLOOD PRESSURE REGULATION
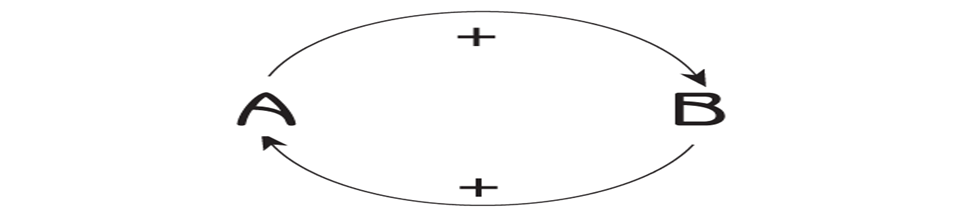
POSITIVE FEEDBACK
• Strengthens or reinforces a change.
• Makes abnormal values more abnormal.
• Produces ‘Vicious Cycle’.
• But in body a mild degree of positive feedback can be overcome by the negative feedback control mechanisms of the body, and the vicious cycle fails to develop.
POSITIVE FEEDBACK LOOP
EXAMPLE: POSITIVE FEEDBACK MEMBRANE DEPOLARISATION
POSITIVE FEEDBACKS IN BODY
• Action potential
• Clotting of blood
• Parturition
• Release of calcium from SR
• Sexual arousal
• LH surge
Summary
• Homeostasis is involved in continuous monitoring of body’s internal environment with respect to altering external environment
• Components of homeostasis are ESI (Effector, Sensor, Integrator)
• Internal environment is maintained by positive and negative feedback mechanisms
• Most of the homeostasis mechanisms involve negative feedback













0 Comments: